OSGI Groundwork !!
May 9, 2017
The Open Services Gateway Initiative (OSGi) defines an architecture for developing and deploying modular applications and libraries. It is also known as the Dynamic Module System for Java, defines an architecture for modular application development. It is proven to help build, package and maintain robust API’s for Java based Enterprise software components running in the Cloud or On Premise.
It is a specification having various implementations like Eclipse Equinox, Apache Felix, Knopflerfish, ProSyst. There are 5 specifications versions released so far and Latest version 1.8.
Why OSGi:
- Adhoc development: Many a times, there are cases where development team, knowingly/unknowingly, uses the implementation to strengthen the ground rules of development by not exposing implementation.
- Architects are unaware of ground realities: Above mentioned point is most of the times unknown to architects and they don’t look in to each of the implementations.
- Deadlines: Most of the times there are short deadlines on development which don’t allow for structured document.
How it helps:
Considering all of the above points, OSGi enables implementation to be modularised, structured, and loosely coupled. Also, OSGi benefits faster deliverable considering “Semantic versioning”- which in simple words: Various versions of packages should reflect the evolution of these packages. For this reason, a change in the first (major) part of the version signals backward incompatible changes to the artifacts. That is, going from version 1.5 to version 2 signals that another artifact compiled against 1.5 up to (but not including) version 2 of that initial artifact is not compatible with the new version of the initial artifact.
Let’s go through an example of how OGSi services to manage and consumer concept demonstration.
And before we proceed, here are the list of prerequisites:
- Java
- Eclipse
Here are the steps.
- Create 3 new project as “plug-in project” name it as listed below.
- Summation Service. (Service and Implementation exposure)
- Subtraction Service. (Service and Implementation exposure)
- Calculator. (Consumer of above mentioned services)
- In Summation service, let’s create “SummationService” which is an Interface and “SummationServiceImpl” which is an implementation class to perform sum activity.
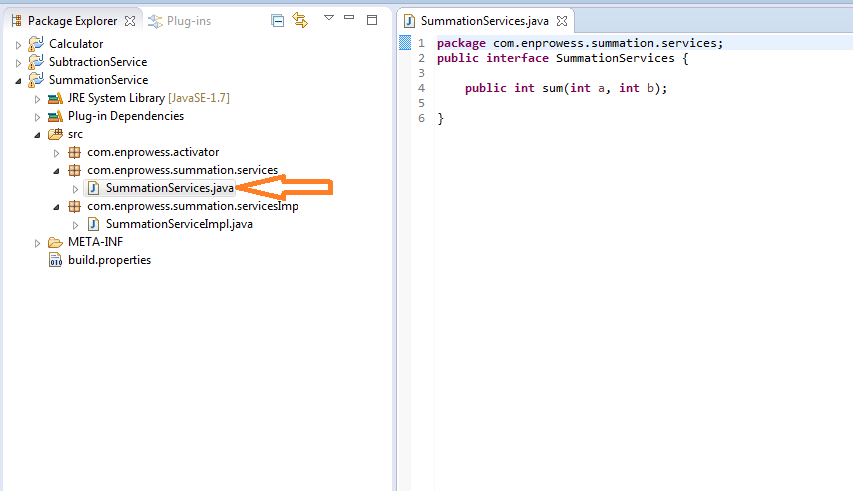
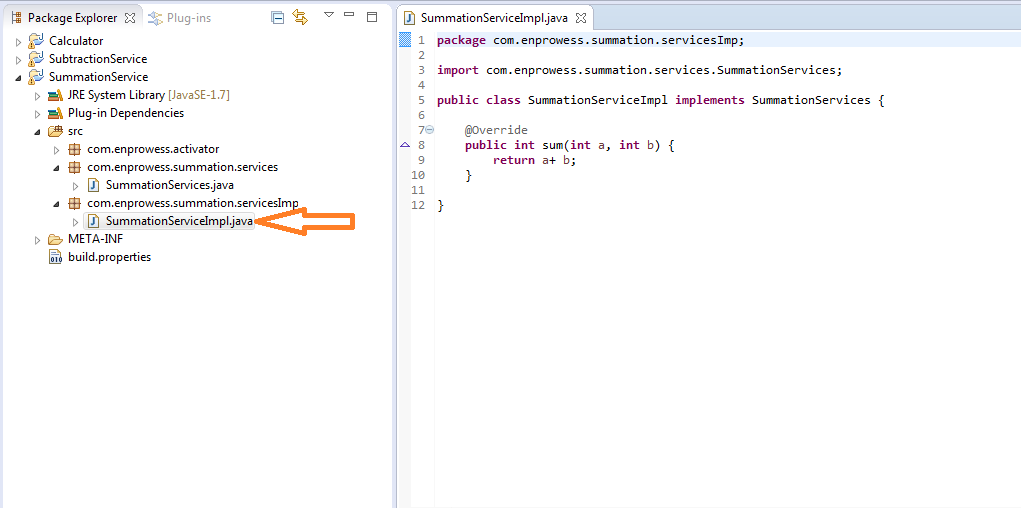
- Modify Activator Class of “SummationService” and Register “SumService” in start method.
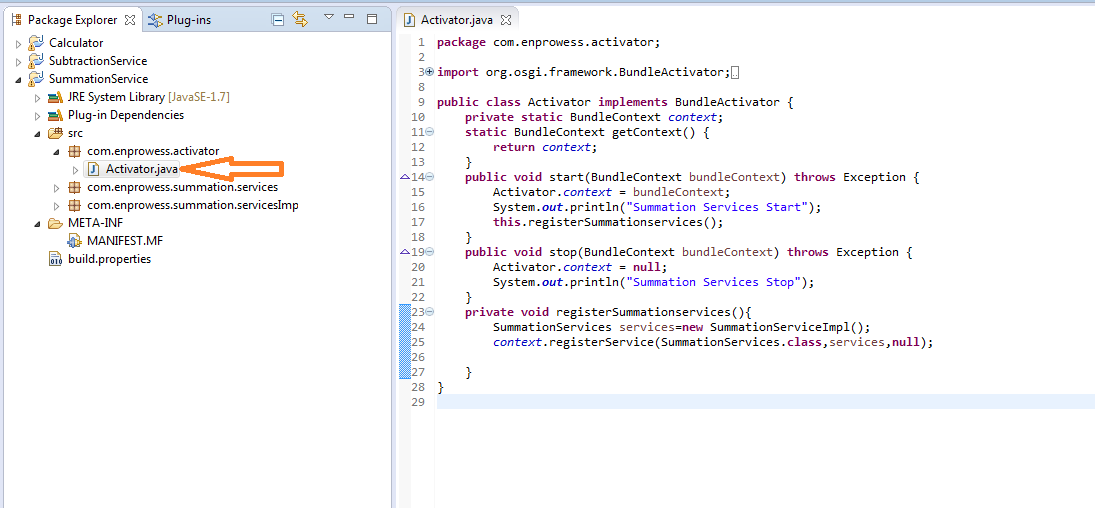
Activator class:- Activator class which implements the BundleActivator interface. An instance of this class is created when the plug-in gets activated. Its start() and stop() methods are called whenever the plug-in is started or stopped.
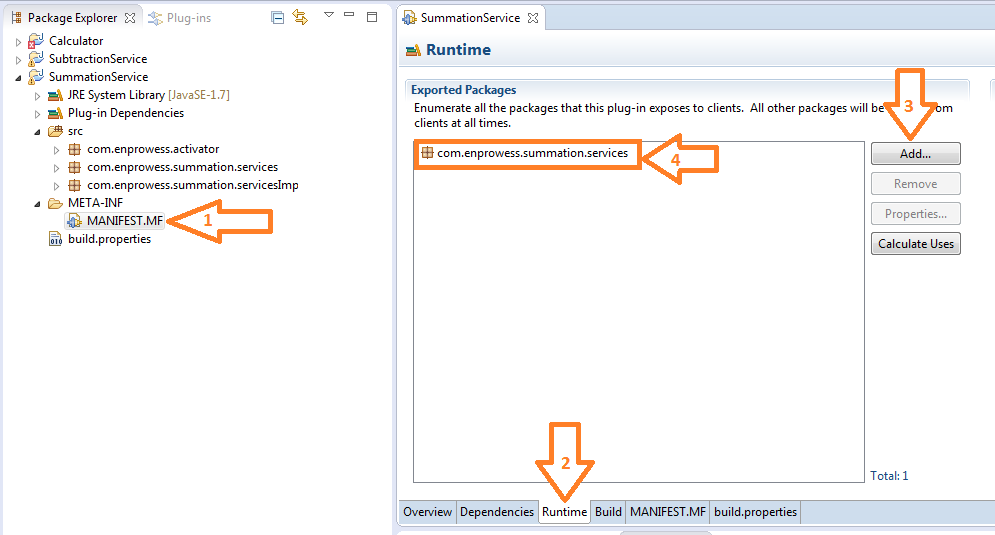
- Add service Packages which consumer needs to access. Here we used “enprowess.summation.service” for SummationService.
Go to META-INF -> MANIFEST.MF -> Runtime -> Add -> “com.enprowess.summation.service”
- In SubtrationService plug-in project, let’s an interface “SubtrationService” and “SubtractionServicesImpl” class to perform subtraction activity. Follow same as step 2
- Modify “Activator” Class -> SubtractionServices and perform subtraction. Register “SubtractionService” in start method.
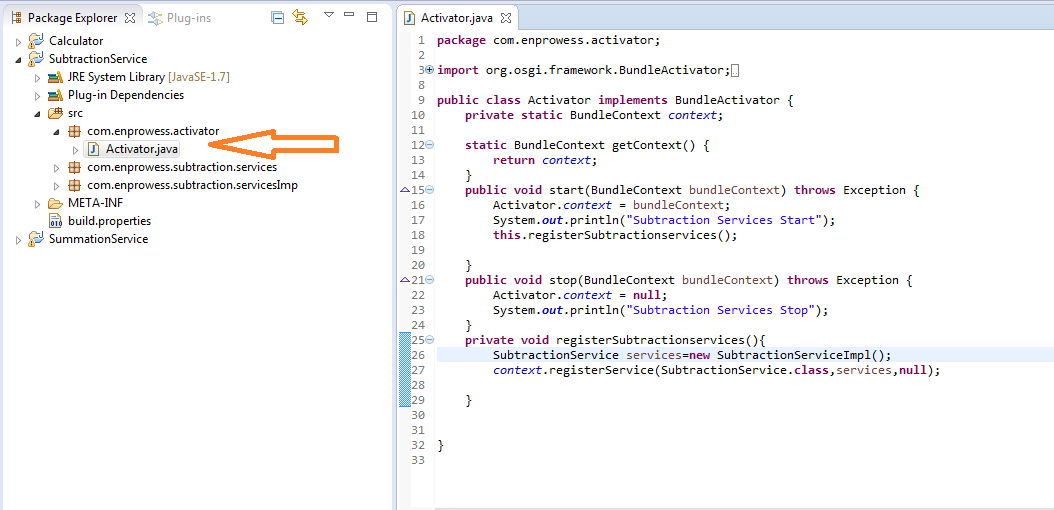
- For “SubtractionServices” project, Add services Package “com.enprowess.subtraction.service” which we want to allow consumer to access.
Same as step 4.
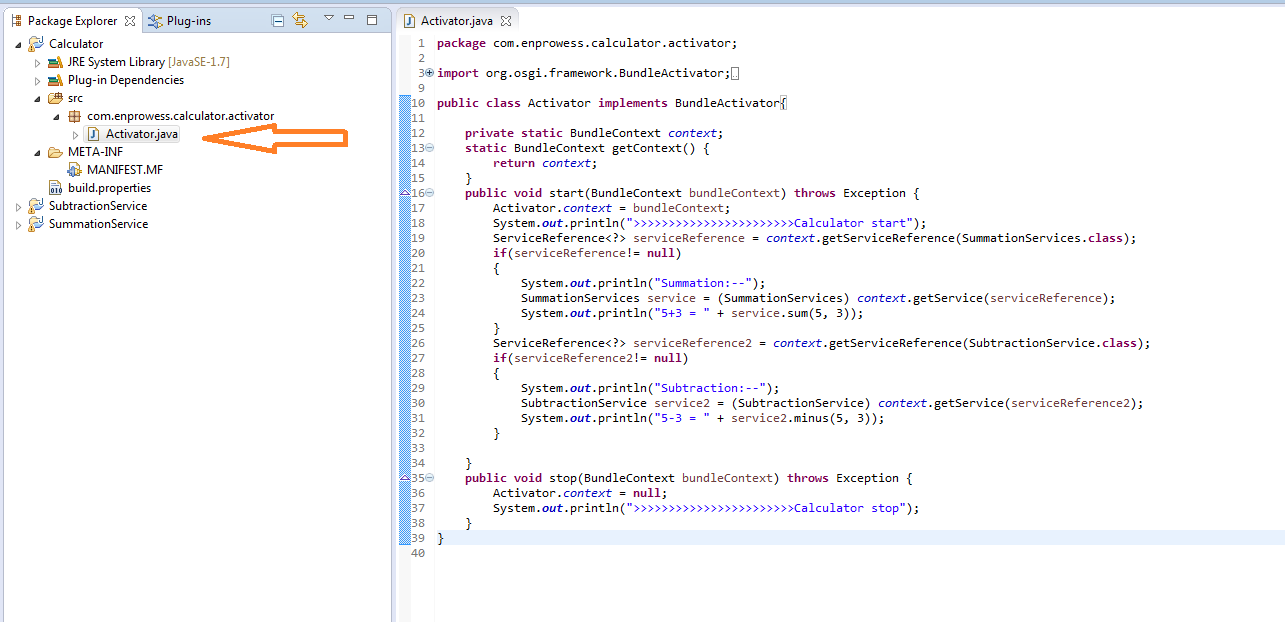
- In Calculator project, modify default activator class.
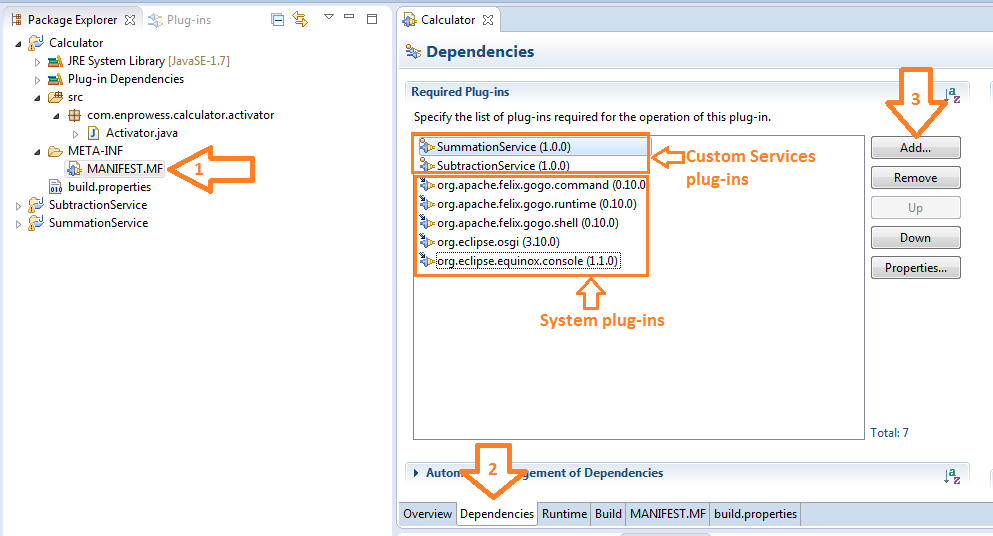
- Now let’s add all the plug-ins required for project.
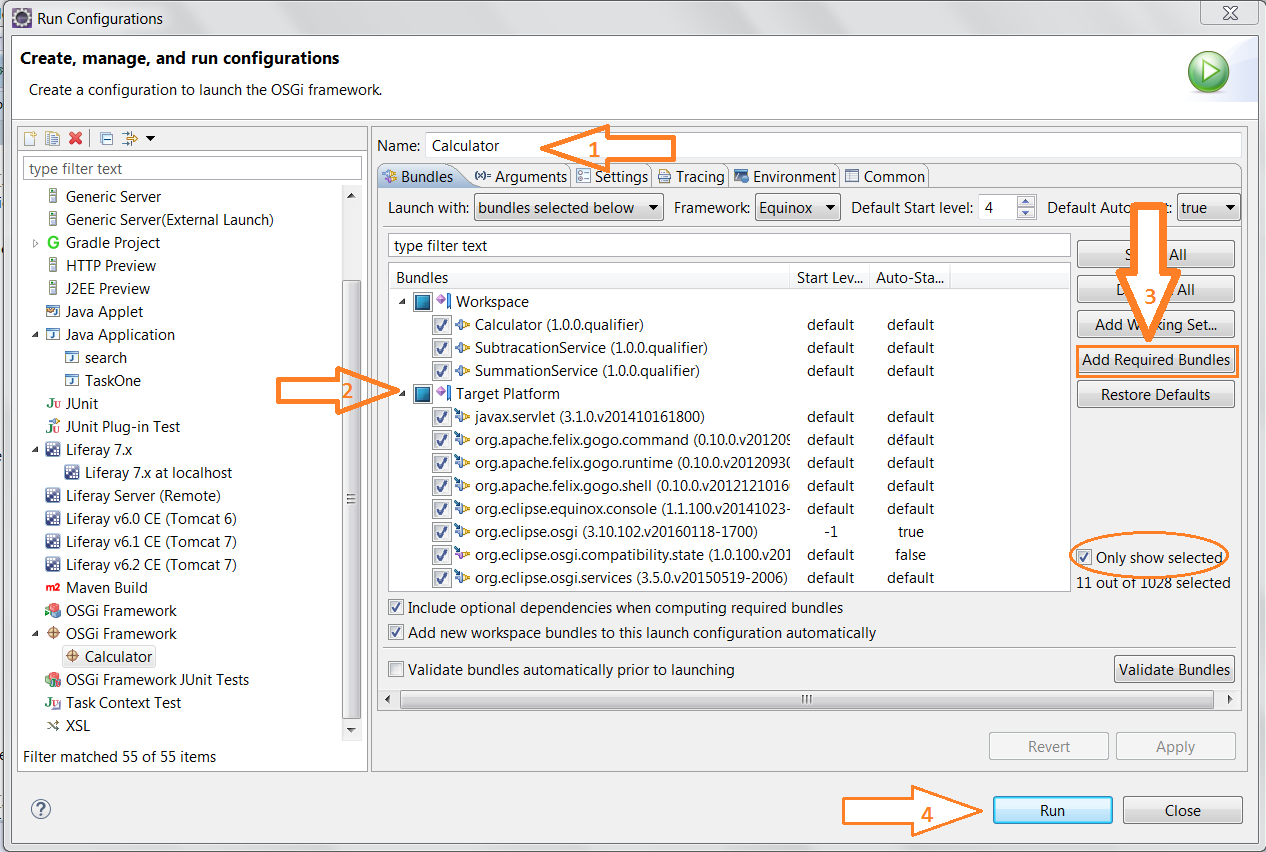
- Set up the Run Configurations. Here we are using GOGO command shell dependencies.
Right click on “Calculator” module and click on “Run As -> Run Configurations”
Click on “OSGi Framwork” – “New”.
Provide appropriate name for this configuration. Here it is given as “Calculator”.
Uncheck “Target Platform” and click on “Add Required Bundles” which should automatically add the required references. You may click on “Only show selected” just to view final list of dependencies.
- Upon execution, the Output looks like below:
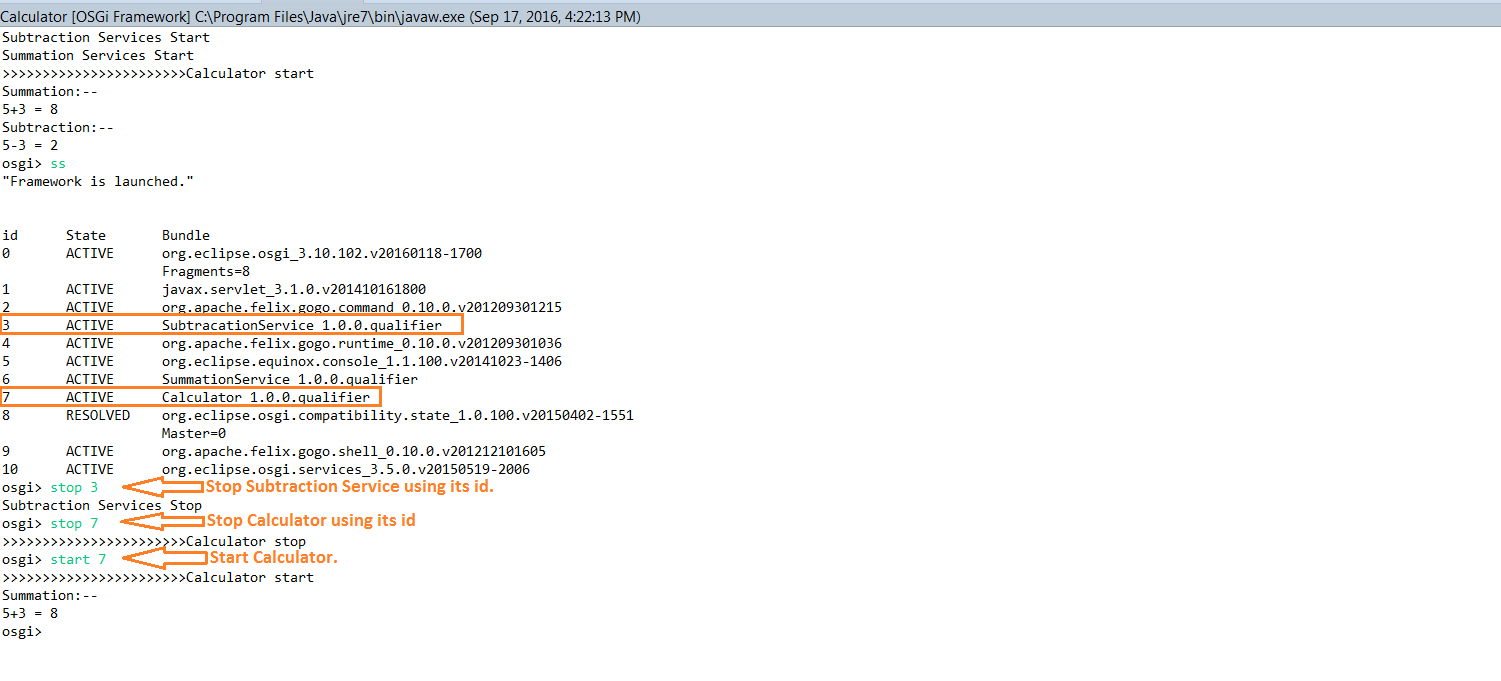
Important commands:
ss: list of services.
Start <id>: It starts the service/module mentioned by id from ‘ss’ command.
Stop <id>: It stop the service/module mentioned by id from ‘ss’ command.
To summarize, we have seen in above example, how do we use osgi modularization. Decoupling of modules gives faster turnaround time and ultimately helps business to release features and fixes at faster pace.
Blog By,
Sejal Patel
Software Engineer